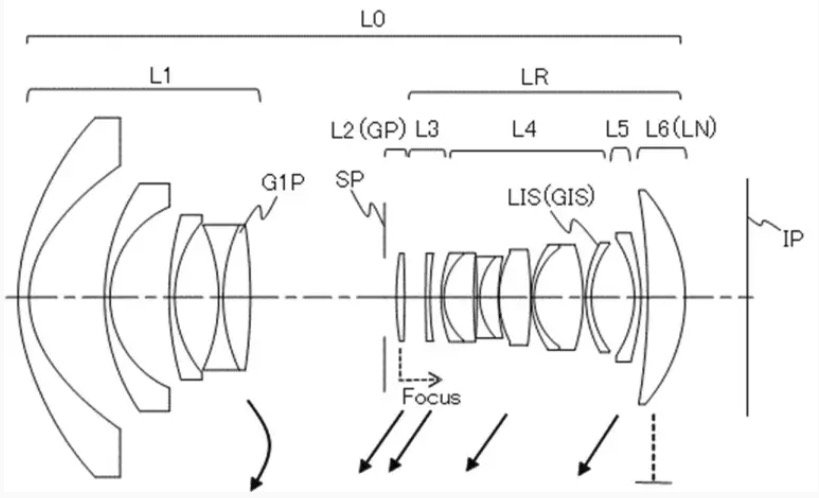
Here is a new Canon patent application, as usual for RF-mount lenses. Canon patent application…
Canon Patent for Improved Auto-Focusing Method
Canon secured a patent (EP20120151498) for an auto-focusing algorithm (and unit) to speed up auto-focusing operations of a digital DSLR while tracking moving objects (at least this is what I understood by reading the patent). Is this the next generation of Canon’s AF systems?
A focus control method is provided that performs focus control by sensing a plurality of images of an object while moving a position of a focusing lens and determining in-focus positions in auto focusing areas located at a plurality of positions. The focus control method calculates an in-focus position of the focusing lens based on the focusing lens position at the time of reading an image signal of each of the auto focusing areas and a degree of focused state of each of the auto focusing area that is based on the image signal of each of the auto focusing areas.
The patent aims at resolving issues caused by the rolling shutter method used to control an electronic shutter. This works as follows:
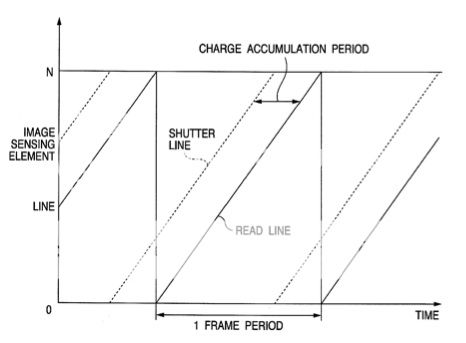
Conventionally an electronic shutter control method referred to as a so-called “rolling shutter” is used […] as an image sensing control method of a CMOS-type image sensing element. In an image sensing operation using the rolling shutter, first, a plurality of pixels that were arranged two-dimensionally are scanned sequentially in sectional units such as lines, to read an electric charge from each pixel and reset each pixel. After the lapse of a predetermined time (charge accumulation period or exposure time) that starts immediately after the reset, the plurality of pixels are rescanned in a similar manner to when they were reset, thereby reading a charge from each pixel, and the read charge (image signal) is output. When sensing a moving image, the above described operation is performed in one-frame periods.
This method has some issues:
[…] when sensing an image using the rolling shutter as described above, there is a time difference of one frame between the timing for scanning the first pixel line and the timing for scanning the last pixel line. More specifically, in an image of one frame, scenes with a time difference between the top and bottom of the frame coexist. Therefore, when controlling an image sensing element using the rolling shutter system to sense a moving object, the image is distorted between the top and bottom of the image.
And while there are methods to tackle the issue, they are not fully satisfying. The patent names a method that performs image sensing continuously while moving the lens. But this method still has some problems:
[…]when acquiring AF evaluation values at a plurality of positions in an image, the position of the focusing lens corresponding to the AF evaluation value of the AF area from which the image signal is first read differs from the position of the focusing lens corresponding to the AF evaluation value of the AF area from which the image signal is last read. As a result, a deviation occurs with respect to the position of the focusing lens that is judged to be in-focus for each AF area.
Here is the flow-diagram of the patented method:
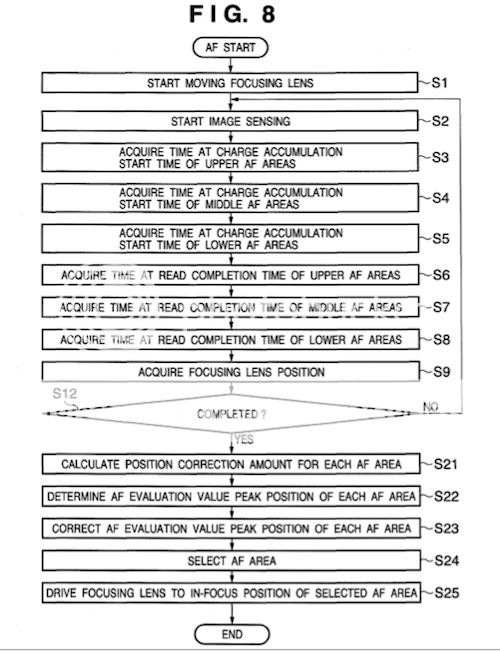
And the full text of the disclosure (written in Patentian Language, not really easy to read):
DISCLOSURE OF INVENTION
The present invention has been made in consideration of the above situation, and has as its object to increase focusing accuracy when performing autofocus control using an image sensing element whose charge accumulation periods differ for a plurality of AF areas while continuously moving a focusing lens.
According to the present invention, the foregoing object is attained by providing a focus control method that carries out focusing control by sensing a plurality of images of an object while moving a position of a focusing lens and determining in-focus positions of auto focusing areas that are located at a plurality of positions, wherein the focus control method calculates an in-focus position of the focusing lens based on a focusing lens position acquired when reading an image signal of each of the auto focusing area and a degree of focused state of each of the auto focusing areas acquired based on an image signal of each of the auto focusing areas.
According to the present invention, the foregoing object is also attained by providing a focus control method that carries out focusing control by sensing a plurality of images of an object while moving a position of a focusing lens and determining in-focus positions of auto focusing areas that are located at a plurality of positions, comprising: a first acquisition step of acquiring read times at which image signals of the respective auto focusing areas are read; a second acquisition step of acquiring a focusing lens position and a time at which the focusing lens position is acquired; a position calculation step of determining focusing lens positions at the read times of the image signals of the respective auto focusing areas based on the read times of the respective auto focusing areas that are acquired in the first acquisition step and the focusing lens position and time that are acquired in the second acquisition step; an evaluation value calculation step of calculating evaluation values that represent degrees of focused states of the respective auto focusing areas based on the image signals of the respective auto focusing areas; and an in-focus position calculation step of calculating an in-focus position of the focusing lens based on the focusing lens positions that are determined in the position calculation step and the evaluation values of the respective auto focusing areas that are calculated in the evaluation value calculation step.
Further, according to the present invention, the foregoing object is also attained by providing A focus control method that carries out focusing control by sensing a plurality of images of an object while moving a position of a focusing lens and determining in-focus positions of auto focusing areas that are located at a plurality of positions, comprising: a first acquisition step of acquiring read times at which image signals of the respective auto focusing areas are read; a second acquisition step of acquiring a focusing lens position and a time at which the focusing lens position is acquired; an evaluation value calculation step of calculating evaluation values that represent degrees of focused states of the respective auto focusing areas based on the obtained image signals; an in-focus position calculation step of calculating in-focus positions of the focusing lens of the respective auto focusing areas based on the focusing lens position acquired in the second acquisition step and the evaluation values of the respective auto focusing areas that are calculated in the evaluation value calculation step; a correction step of correcting the in-focus positions of the respective auto focusing areas based on the read times of image signals of the respective auto focusing areas that are acquired in the first acquisition step, the focusing lens position and time that are acquired in the second acquisition step, and the in-focus positions of the auto focusing respective areas calculated in the in-focus position calculation step; and an in-focus position determination step of determining an in-focus position of the focusing lens based on the in-focus positions that are corrected in the correction step.
Furthermore, according to the present invention, the foregoing object is also attained by providing a focus control unit that carries out focusing control by sensing a plurality of images of an object while moving a position of a focusing lens and determining in-focus positions of auto focusing areas that are set at a plurality of positions, comprising: a controller that controls an in-focus position of the focusing lens based on a focusing lens position acquired when reading an image signal of each of the auto focusing area and a degree of focused state of each of the auto focusing areas acquired based on an image signal of each of the auto focusing areas.
Further, according to the present invention, the foregoing object is also attained by providing a focus control unit that carries out focusing control by sensing a plurality of images of an object while moving a position of a focusing lens and determining in-focus positions of auto focusing areas that are set at a plurality of positions, comprising: a position calculation unit that acquires read times at which image signals of the respective auto focusing areas are read and a focusing lens position and a time at which the focusing lens position is acquired, and determines focusing lens positions at the read times of the image signals of the respective auto focusing areas based on the read times of the auto focusing areas and the focusing lens position and time; an evaluation value calculation unit that calculates evaluation values that represent degrees of focused states of the respective auto focusing areas based on the image signals of the respective auto focusing areas; and an in-focus position determination unit that determines an in-focus position of the focusing lens based on the focusing lens position that is acquired by the position calculation unit and the evaluation values of the respective auto focusing areas that are calculated by the evaluation value calculation unit.
Further, according to the present invention, the foregoing object is also attained by providing a focus control unit that carries out focusing control by sensing a plurality of images of an object while moving a position of a focusing lens and determining in-focus positions of auto focusing areas that are set at a plurality of position, comprising: an acquisition unit that acquires read times at which image signals of the respective auto focusing areas are read and a focusing lens position and a time at which the focusing lens position is acquired; an evaluation value calculation unit that calculates evaluation values that represent degrees of focused states of the respective auto focusing areas based on the obtained image signals; an in-focus position determination unit that determines in-focus positions of the focusing lens of the respective auto focusing areas based on a focusing lens position acquired by the acquisition unit and evaluation values of the respective auto focusing areas that are calculated by the evaluation value calculation unit; and an in-focus position correction unit that corrects the in-focus positions of the respective auto focusing areas based on the read times of the image signals of the respective auto focusing areas and the focusing lens position and time that are acquired by the acquisition unit and an in-focus positions of the respective auto focusing areas that are determined by the in-focus position determination unit, and determines an in-focus position of the focusing lens based on the corrected in-focus positions.
Other features and advantages of the present invention will be apparent from the following description taken in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, in which like reference characters designate the same or similar parts throughout the figures thereof.