Canon patent to reduce moire artefacts in image data
Here is another Canon patent application I think might go into production.
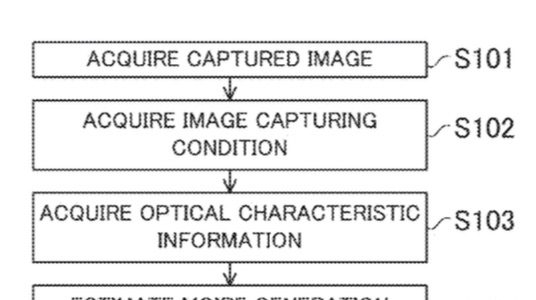
Canon patent application US20170358058 describes an algorithm to estimate and eventually correct moire artefacts in image data.
From the patent abstract:
An image processing apparatus includes an estimator which estimates a moire component included in an image based on optical characteristic information, a determiner which determines a correction amount based on the estimated moire component, and a corrector which corrects the image so as to reduce the moire component included in the image based on the correction amount.
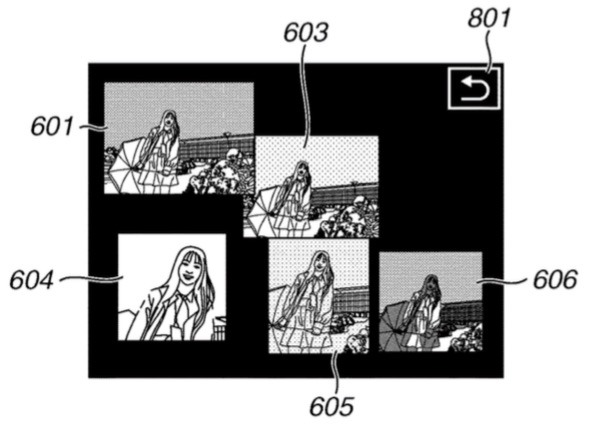
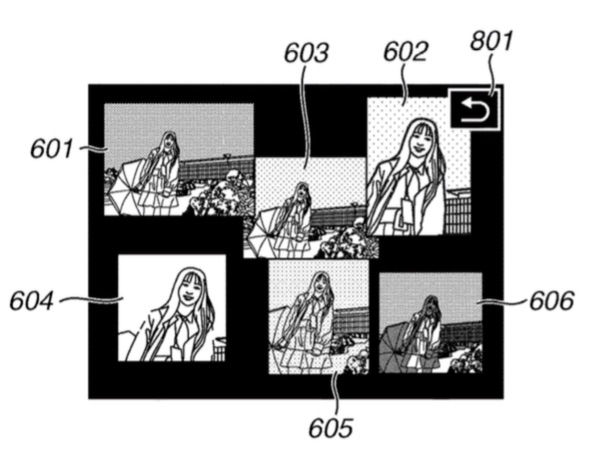
Canon files a huge amounts of patent applications. That does not mean all the patents we spot will go into production. However, some patents actually have a chance to made it into production and I am trying to find them, like this patent to improve burst rate by compressing raw files, or this one describing an improved way to review photos from a sequential shot, or the patent that describes technology to improve wireless communication while reducing power consumption.

 Canon patent application
Canon patent application  Canon patent application
Canon patent application  Here is a Canon patent (United States Patent
Here is a Canon patent (United States Patent