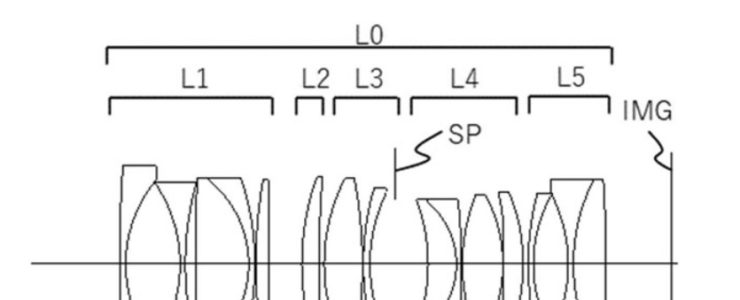
Canon Patent: 11mm F2, 13mm F2, 22mm F2, And 30mm F2 Lenses For RF-S Mount
Here is a new Canon patent application, for a bunch of fast primes for the RF-S mount.
Canon patent application P2023130885 (Japan, published 9/21/2023) discusses optical formulas for RF-S mount prime lenses:
- 11mm F2
- 13mm F2
- 22mm F2
- 30mm F2
From the patent literature:
An object of the present invention is to provide a rear focus optical system that is compact and capable of good aberration correction.
BACKGROUND ART
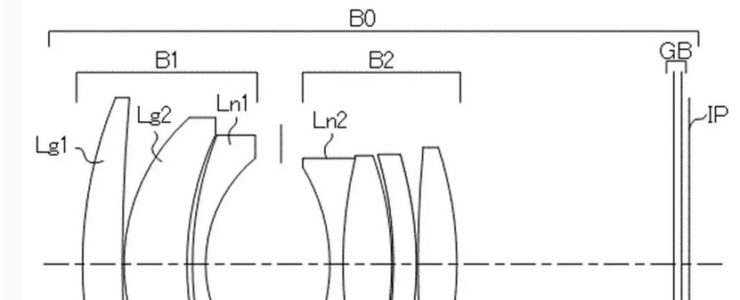
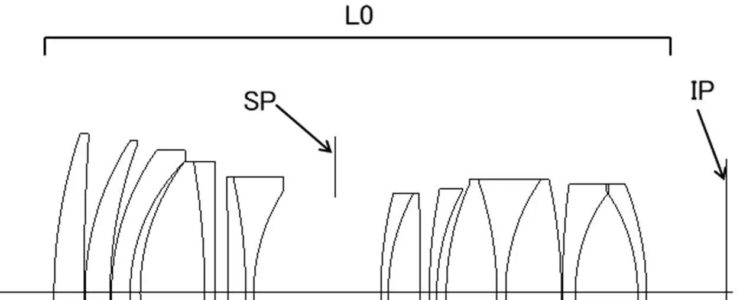
In imaging, it is required to suppress the generation of noise during zooming and focusing. In order to suppress noise during focusing, the rear focus (inner focus) method, in which focusing is performed by moving the lens group closest to the image side than the lens group closest to the object side, is recommended because it provides the best sound isolation effect from the object side lens. suitable.
Rear focus type optical systems are also required to be compact and have good aberration correction. In order to realize such an optical system, it is necessary to appropriately set the lens arrangement and the focal length of each lens.
The present invention provides a rear focus type optical system that is compact and capable of good aberration correction, and an imaging device equipped with the same.
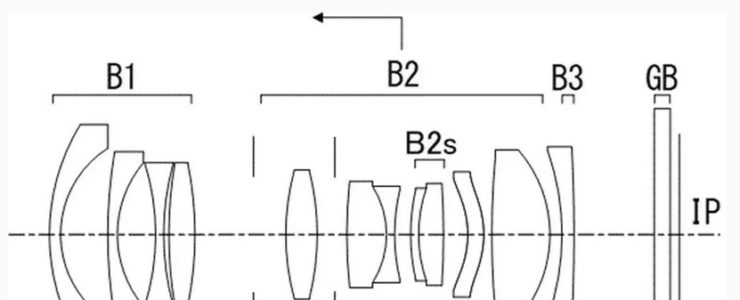
Example 1
- Focal length: 13.40
- F value: 2.06
- Half angle of view: 43.01
- Image height: 12.50
- Total length: 77.83
- Back focus: 12.43
Example 2
- Focal length: 11.30
- F value: 2.06
- Half angle of view: 47.89
- Image height: 12.50
- Total length: 77.85
- Back focus: 12.44
Example 3
- Focal length: 22.00
- F value: 2.06
- Half angle of view: 29.60
- Image height: 12.50
- Total length: 72.85
- Back focus: 12.444
Example 4
- Focal length: 30.52
- F value: 2.06
- Half angle of view: 22.27
- Image height: 12.50
- Total length: 75.88
- Back focus: 14.49
More Canon patents are listed here.
[via asobinet]