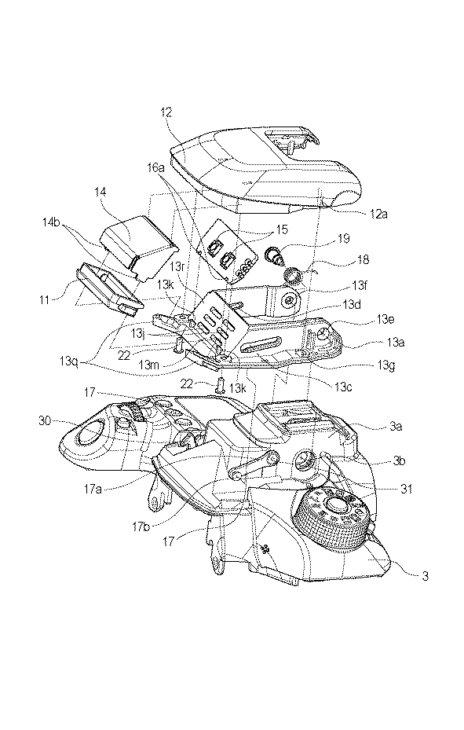
Latest Canon Patent Applications (celestial AF, improved viewfinder, IS on tilt-shift, telephoto)
US Patent Application 20490158760 discusses how to get better autofocus performance when picturing objects in the sky, like the moon.
In recent years, the number of pixels in image capturing apparatuses such as cameras and videos has increased, a slight defocus state of an image has become conspicuous and, more precise focusing is desired. This is the same in shooting an image of celestial bodies (stars, moon, and so forth) in the night sky.
Focusing on celestial bodies is performed by calculating a focus position at which an area represented by high brightness signals is strictly minimized when regarding each celestial body as a point light source. As stars and the moon which are subjects in astrophotography at night are located substantially at infinity and there are specific exposure settings for astrophotography, there is an independent shooting mode for astrophotography different from other scene modes. Hereinafter, a mode for shooting the moon as the main subject is referred to as a “moon shooting mode”.
Normally, the focus position at which an object located substantially at infinity is in focus is uniquely determined by performing infinite focus adjustment in individual image capturing apparatus. However, due to a difference between temperature at a time of the infinite focus adjustment and temperature of the image capturing apparatus at a time of actually shooting a celestial body, a difference in posture, and so forth, the focus may shift during shooting. For this reason, it is necessary to often adjust focus even during shooting a celestial body whose distance from the image capturing apparatus does not substantially change during shooting.
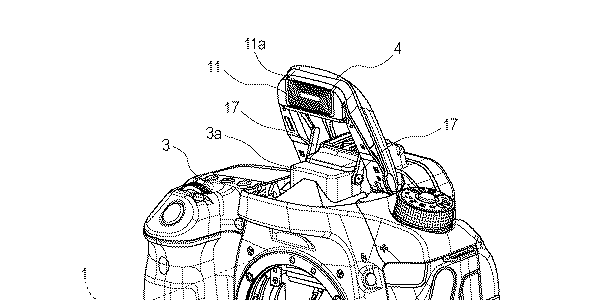
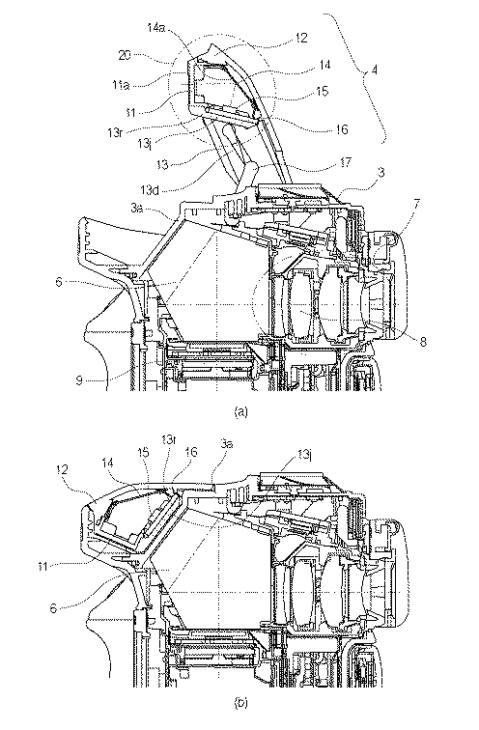
Japan Patent Application 2019-078959 describes am improved viewfinder which improves on aberrations and magnification while maintaining a long eyepoint.
[…] the focal length of the eyepiece is about 65 mm, and the finder magnification is about 0.8 or less when the standard lens with a focal length of 50 mm is mounted as a photographing lens.
Therefore, in a camera using a so-called APS-C size sensor in which the size of the image circle is smaller than a 35 mm film, the finder image becomes smaller than the conventional silver halide film camera.
Further, in the prior art disclosed in Patent Document 2, although the finder magnification is as high as about 1 time, it is difficult to sufficiently correct axial chromatic aberration and lateral chromatic aberration.
Therefore, an object of the present invention, while increasing the magnification while maintaining high optical performance, is to provide a finder optical system capable of ensuring long eye point.
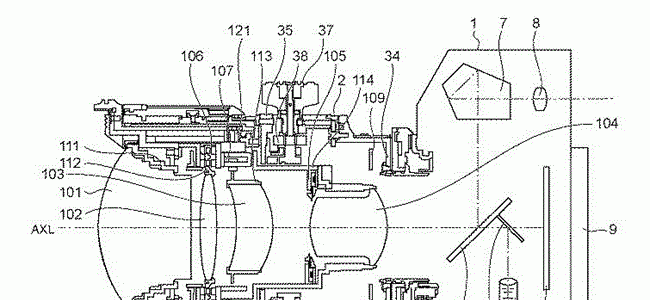
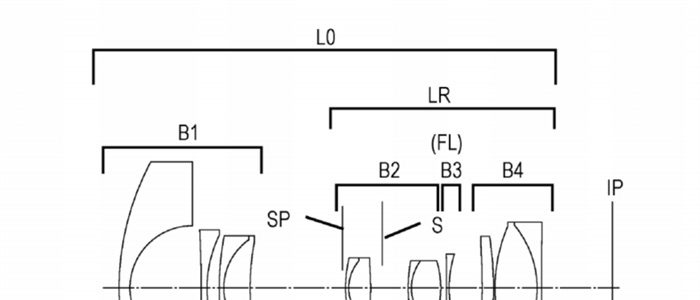
Japan Patent Application 2019-078903 describes how to implement an image stabilisation system on a tilt-shift lens while also lowering the power consumption.
It is an object of the present invention to provide a lens apparatus capable of reducing the power consumption while being able to shoot under an eyebrow and correct the shake, and an image pickup apparatus using the same.
To achieve the above object, a lens device of the present invention,
– an optical system comprising a plurality of lenses,
– the shake correction lens of the plurality of lenses the optical system A – driving unit for moving in a direction crossing the optical axis;
A tilt unit for tilting the optical system and a control unit for controlling the drive unit are provided, and the control unit is configured to make the tilt amount of the optical system generated by the tilt unit smaller than a predetermined tilt amount. When the first tilt amount and the shake amount applied to the optical system are the first shake amount larger than a predetermined shake amount, the shake correction lens is in a direction crossing the optical axis. The drive unit is controlled to move in a direction intersecting the optical axis with a first drive amount smaller than the maximum drive amount of the shake correction lens
According to the present invention, it is possible to provide an imaging apparatus using the lens apparatus and which capable of reducing power consumption as well as a possible tilt shooting and shake correction .
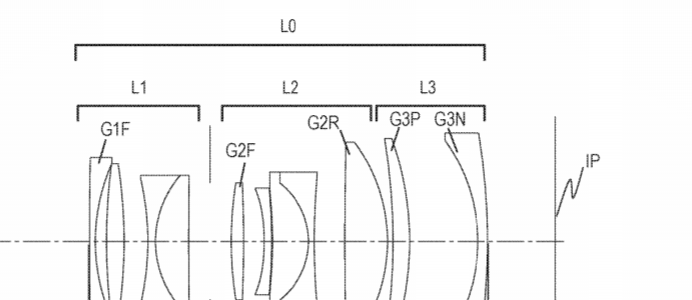
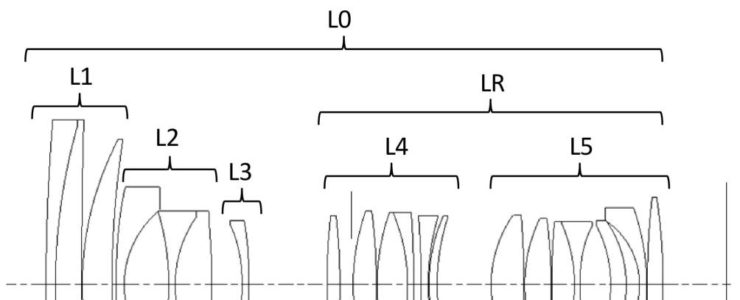
Japan Patent Application 2019-078948 describes various optical formulas for telephoto lenses and how to reduce chromatic aberrations.
- focal length 392.55
- f-number 2.90
- half angle of view 3.15
- image height 21.64
- total lens length 372.00
- BF 60.70
- focal length 292.46
- f-number 2.90
- half angle of view 4.23
- image height 21.64
- lens total length 273.98
- BF 62.03
- focal length 488.82
- F number 4.10
- half angle of view 2.53
- image height 21.64
- lens total length 411.90
- BF 71.62
- focal length 778.70
- F number 5.83
- Half angle of view 1.59
- image height 21.64
- lens total length 486.03
- BF 71.54
US Patent Application 20190155003 describes optical formulas for more telephoto lenses. As with the previous patent application, here too reduction of chromatic aberrations is discussed.
In an ultra-telephoto lens, generally, the longer the focal length, the more axial chromatic aberration or magnification chromatic aberration occurs. As a technique for excellently correcting these types of chromatic aberration, a technique for increasing the number of lenses placed on an object side and causing the lenses to share the action of correcting chromatic aberration is known. However, the effective diameter of a lens placed on the object side of the ultra-telephoto lens is likely to be large. Thus, if an attempt is made to correct chromatic aberration by the above technique, the weight of an imaging optical system increases.