Canon Patent: Quad Pixel Phase Detection Auto-Focus
Here is a new and definitely interesting Canon patent application: Quad Pixel Phase Detection AF. It’s not the first patent for this technology.
Canon patent application 2023166867 (Japan, published 11/22/2023) discusses methods and technology for Canon’s next generation autofocus technology, Quad Pixel Detection AF.
From the patent literature:
- [Problem] To improve the performance of focus detection in focus detection using an image plane phase difference method that uses signals output from image sensors having different vertical and horizontal lengths.
- TECHNICAL FIELD
The present invention relates to an image sensor in which a pixel section having a plurality of photoelectric conversion sections is two-dimensionally arranged, and an image sensor equipped with the image sensor. - BACKGROUND ART
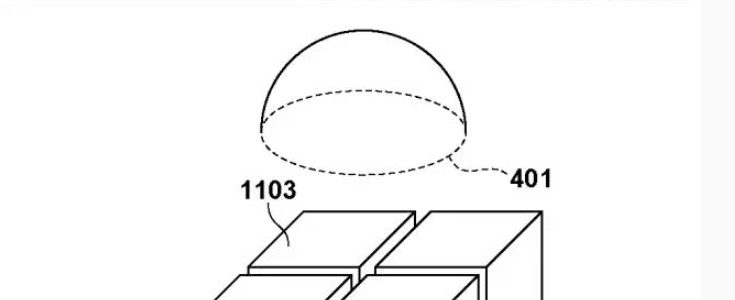
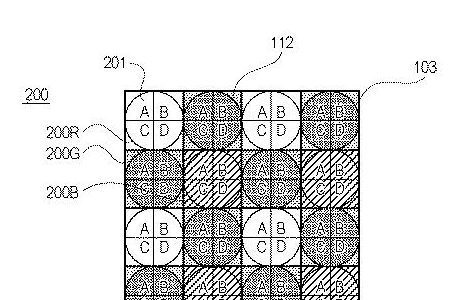
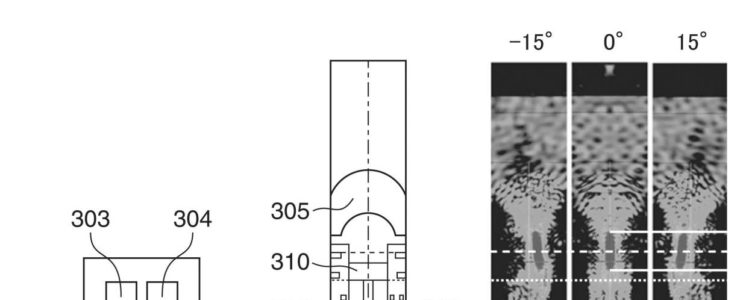
Conventionally, as one of the focus detection methods performed in an imaging device, a pair of pupil division signals are acquired using focus detection pixels formed on an image sensor, and a focus detection method using a phase difference method is used. A so-called imaging plane phase difference method for performing detection is known. - As an example of such an imaging surface phase difference method, there is an imaging device using a two-dimensional imaging element in which one microlens and a plurality of divided photoelectric conversion sections are formed for one pixel. It is disclosed in Patent Document 1. The plurality of photoelectric conversion units are configured to receive light transmitted through different regions of the exit pupil of the imaging lens via one microlens, and perform pupil division. Then, by calculating the amount of image shift from the phase difference signal that is a signal of each photoelectric conversion unit, focus detection using a phase difference method can be performed. Further, by adding up the signals of the individual photoelectric conversion units for each pixel, a normal image signal can be obtained. Further, Patent Document 1 discloses a configuration in which the saturation resistance of the pixel is increased by arranging a plurality of types of pixels having different heights of separation barriers between photoelectric conversion parts in the pixel.
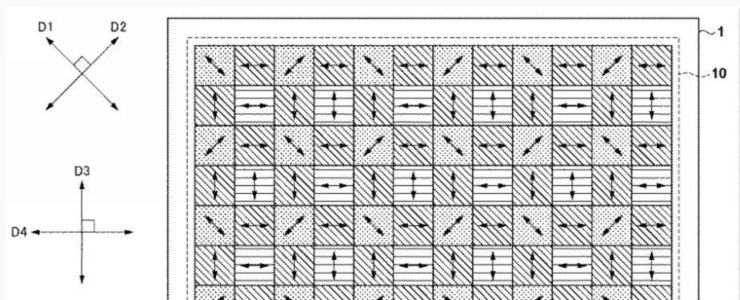
- In such an image sensor, in a configuration in which a plurality of photoelectric conversion units are arranged horizontally within a pixel and the pupil division direction is horizontal, for example, when the subject has a horizontal striped pattern, parallax is This may be difficult to see, and focus detection accuracy may deteriorate.
- On the other hand, Patent Document 2 discloses a technique for improving focus detection accuracy by providing two types of arrangement directions of photoelectric conversion units for each microlens and two types of pupil division directions. There is. Furthermore, Patent Document 2 discloses a structure that separates vertically adjacent photoelectric conversion units and a structure that separates horizontally adjacent photoelectric conversion units, and has a structure that allows electric charges to leak to adjacent photoelectric conversion units. It is disclosed that the With this structure, supersaturated charges received in excess of the amount of charge that can be accumulated by one photoelectric conversion section leak and accumulate in different photoelectric conversion sections arranged in a predetermined direction. Even in the case of saturation, horizontal or vertical phase difference focus detection is possible.
- Most conventional image sensors do not have an aspect ratio of 1:1. Therefore, when focus detection pixels using the image plane phase difference method in the vertical direction and focus detection pixels in the horizontal direction are arranged on the image sensor, focus detection using the image plane phase difference method is difficult, especially in the periphery of the image sensor. Performance is biased towards either the vertical or horizontal direction.
- The image sensor described in Patent Document 1 changes the separation state of the photoelectric conversion unit depending on the saturation state of the pixel. Therefore, depending on the aspect ratio of the image sensor, the state of charge crosstalk (a phenomenon in which charge leaks to the adjacent photoelectric conversion unit) between the photoelectric conversion units in the vertical focus detection pixels and the horizontal focus detection pixels respectively occurs. It is not possible to control the above problems and cannot solve the above problems.
- Furthermore, the image sensor of Patent Document 2 does not have a configuration that controls charge crosstalk when the photoelectric conversion section is not saturated, and also controls charge crosstalk between the photoelectric conversion sections according to the aspect ratio of the image sensor. Since there is no mention of the talk rate, the above problem cannot be solved.
- The present invention has been made in view of the above problems, and is intended to improve the performance of focus detection in focus detection using an image plane phase difference method that utilizes signals output from image sensors having different lengths and widths. The purpose is to
More Canon patent applications are listed here.
[via asobinet]