Canon Patent: RF 150-600mm f/8-11 Zoom Lens For EOS R System
A new Canon patent, for a RF 150-600mm f/8-11 zoom lens.
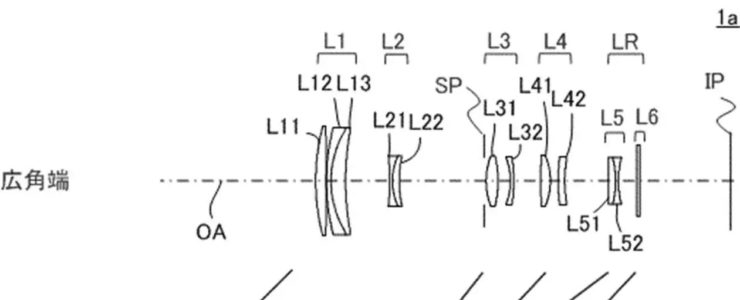
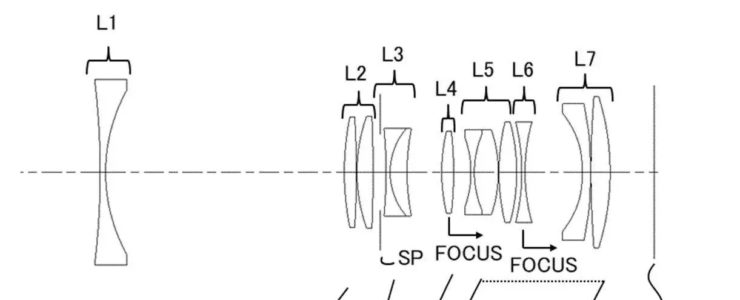
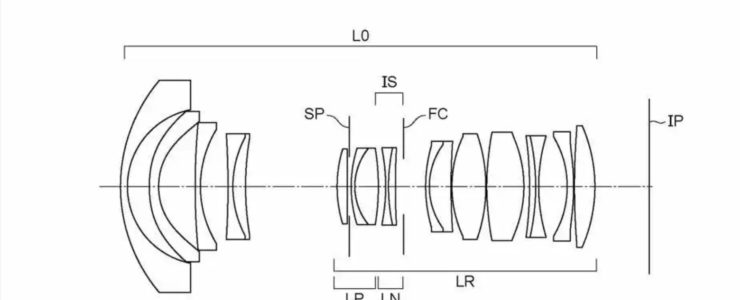
Canon patent application 2022106401 (Japan) discusses optical formulas for a 150-600mm f/8-11 zoom lens for the RF mount.
PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To provide a compact and lightweight zoom lens having high optical performance in the entire zoom range.
Example 1
- Focal length: 103.00-387.89
- F value: 5.82-8.24
- Half angle of view: 11.86-3.19
- Image height: 21.64
- Overall length: 183.21-258.38
- Back focus: 39.88-81.93
Example 2
- Focal length: 153.00-581.90
- F value: 8.00-11.31
- Half angle of view: 8.05-2.13
- Image height: 21.64
- Overall length: 274.81-354.89
- Back focus: 68.40-126.51
More Canon patent applications are listed here. Some particularly interesting patent applications we think might get into production are these:
- Automatic shutter silencing based on subject and distance
- A bunch of prime lenses for the RF mount
- An improved Electronic Viewfinder
- Patent application for RF 50mm F1.4 and an RF 35mm f/1.4 lenses
- A zoom lens that might be for an EOS R with APS-C sensor
- A smaller IBIS unit.
- A cooling adapter for the RF mount (R5 overheating?)
- A bunch of macro lenses for the RF mount.
- A 8mm f/4 circular fisheye lens for the Canon EOS R system
- A battery grip that works with differently siszed cameras
- A 100-400mm f/5.5-7.1 lens for APS-C cameras. EOS M or DSLR?
- RF 17-70mm lens for EOS R system
- IBIS coming to the EOS M and PowerShot lineup?
- Patent Application: mirrorless camera with large display and virtual control wheel
- Patent Application: IBIS and Lens IS Working Together
- Patent application for high speed mirror movement and control
- Patent application for an RF 14-28mm f/2 lens
- Patent application for an RF 50mm f/1.8 lens
- Patent application for a smart lens cap
- Patent application for celestial auto-focus
- Patent application describing a Pop-Up Flash With LED
- Patent application describing the optical formula for a RF 70-300mm F/4-5.6 IS lens for EOS R systems
- Patent application describing how to improve burst rate by compressing raw files
- Patent application describing a new way to review photos from a sequential shot
- Patent application that describes technology to improve wireless communication while reducing power consumption
- Patent application to spot and reduce moire artefacts in image data
- Patent application for weather sealed lens adapter
- Patent application for AI powered predictive camera control system
- Patent application for 18-55mm kit lens with LCD display
- Patent application to reduce noise in image files
[via asobinet]